Core Testing
Pimcore uses Codeception for testing its core features.
To execute core tests, Pimcore provides a docker-compose.yaml file to create a setup for running the tests.
The docker images are based on the debug images, thus it is also possible to debug the tests using xdebug. Make sure, that path mappings are applied correctly though
Requirements
dockeranddocker composeinstalled on your system.- Pimcore git repository cloned locally
Preparations
- Change to
tests\bindirectory of the Pimcore repository - Execute
./init-tests.sh, this does:- Running
docker compose up -dand setting up all necessary services (like db and redis). Pimcore source code files are mounted into docker container, so you can change files and test the changes right away. - Copying some files from
.github\ci\fileto prepare system for executing the tests (actually same as for github actions) - Executing
composer installto install all dependencies - Print out further instructions
- Running
Now the system is ready and tests can be executed inside the docker containers (see also commands below).
After finishing, shutdown docker containers and cleanup volumes with docker compose down -v --remove-orphans.
Executing tests
Run all tests
This will run all tests.
docker compose exec php vendor/bin/codecept run -c . -vvv
Only run a specific suite
Only runs the Model tests. For a list of suites see the list below.
docker compose exec php vendor/bin/codecept run -c . Model -vvv
Only run a specific test group
This can be a subset of a suite. You also have the option to provide a comma-seperated list of groups. For an overview of available groups see the table below.
docker compose exec php vendor/bin/codecept run -c . Model -vvv -g dataTypeLocal
Redis Cache tests
For Redis, the PIMCORE_TEST_REDIS_DSN option is mandatory. If not using the Redis provided by the docker-compose.yaml, set it
to a value that does not conflict to any other Redis DBs on your system.
docker compose exec php vendor/bin/codecept run -c . Cache
Check Logfiles
Don't forget to check logfiles (especially test.log and php.log) inside the docker container when problems occur.
Important Environment Variables
Meaningful default values are set in the shipped docker-compose.yaml. Can be modified as needed.
| Env Variable | Example | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| APP_ENV | test | Test environment |
| PIMCORE_TEST | 1 | important this will switch several directories (like /var/classes) |
| PIMCORE_TEST_SKIP_DB | 1 | Skips DB setup. This does not skip the db-related tests but it reduces the setup time for tests that don't need a database. |
| PIMCORE_TEST_REDIS_DSN | redis://localhost | required for REDIS tests |
Suites
The tests are organized into suites, each one covering specific areas of the core.
| Suite name | Description |
|---|---|
| Cache | Cache tests |
| Model | Dataobject tests |
| Service | Test covering common or shared element tasks (versioning, ...) |
| Unit | Other tests (may need restructuring) |
| ... |
Groups
The following table lists all groups currently used by Pimcore's core tests. If you extend the tests or write new ones please tag them accordingly.
| Group | |
|---|---|
| cache-cli | Cache cli tests |
| cache.core.array | Cache Array handler tests |
| cache.core.db | Cache DB handler tests |
| cache.core.file | Cache File handler tests |
| cache.core.redis | Cache Redis handler tests |
| cache.core.redis_lua | Cache Redis handler tests with LUA enabled |
| dataTypeLocal | Dataobject - datatype tests |
| model.relations.multipleassignment | Dataobject - "allow multiple assignments" tests |
| ... |
Useful command line options
Useful examples:
| Option | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| --group (-g | --group dataTypeLocal | Only execute specified list of groups |
| --skip (-s) | --skip cache,rest | Skip Cache and Rest Tests |
| --skip-group (-x) | --skip-group cache.core.file | Skip file cache tests |
| --fail-fast | --fail-fast | Stop on first error |
| ... |
See Codeception Commands for more options.
Providing new tests & extending existing ones
In general, contributions in form extending and improving tests is highly appreciated. Please follow the structure and principles described above.
If you have the extend the data model then please have a look at Model.php. There you will find all class definitions used for testing.
Perform PHPStan Analysis
First, get a copy of this sample configuration file and place it in your root directory.
Add dependencies:
# minimum
composer require "phpstan/phpstan:^0.12" "phpstan/phpstan-symfony:^0.12"
# required if you want to do a full analysis
composer require "elasticsearch/elasticsearch:^7.11" "composer/composer:*"
Run
TMPDIR=/tmp/[dedicateddir] ./vendor/bin/phpstan analyse --memory-limit=-1
where /tmp/[dedicateddir] must be a writable temporary directory.
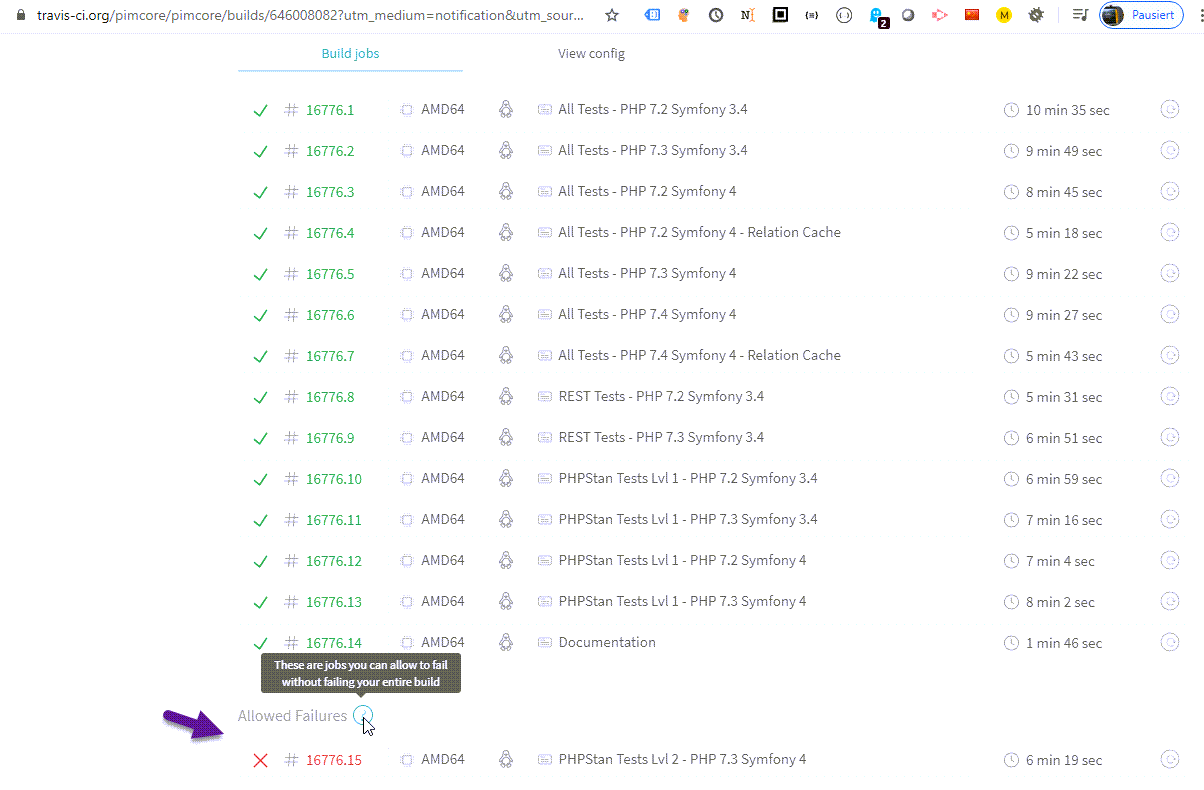
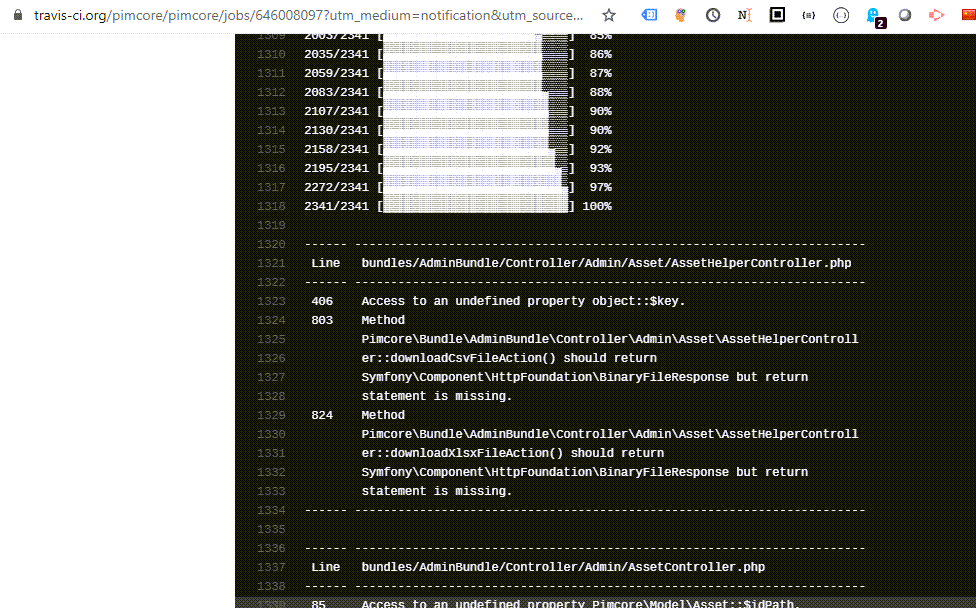
Open the build log and check for problems.
PHPStan Baseline Feature
PHPStan can create a baseline file, which contain all current errors. See this blog entry.
To generate a new baseline file you have to execute following command:
vendor/bin/phpstan analyse --memory-limit=-1 --generate-baseline
With this baseline file include, we can detect new errors without having to fix all errors first.
PHPStan Level Overview
| Level | Checks |
|---|---|
| 0 | basic checks, unknown classes, unknown functions, unknown methods called on $this, wrong number of arguments passed to those methods and functions, always undefined variables |
| 1 | possibly undefined variables, unknown magic methods and properties on classes with __call and __get |
| 2 | unknown methods checked on all expressions (not just $this), validating PHPDocs |
| 3 | return types, types assigned to properties |
| 4 | basic dead code checking - always false instanceof and other type checks, dead else branches, unreachable code after return; etc. |
| 5 | checking types of arguments passed to methods and functions |
| 6 | check for missing typehints |
| 7 | report partially wrong union types |
| 8 | report calling methods and accessing properties on nullable types |